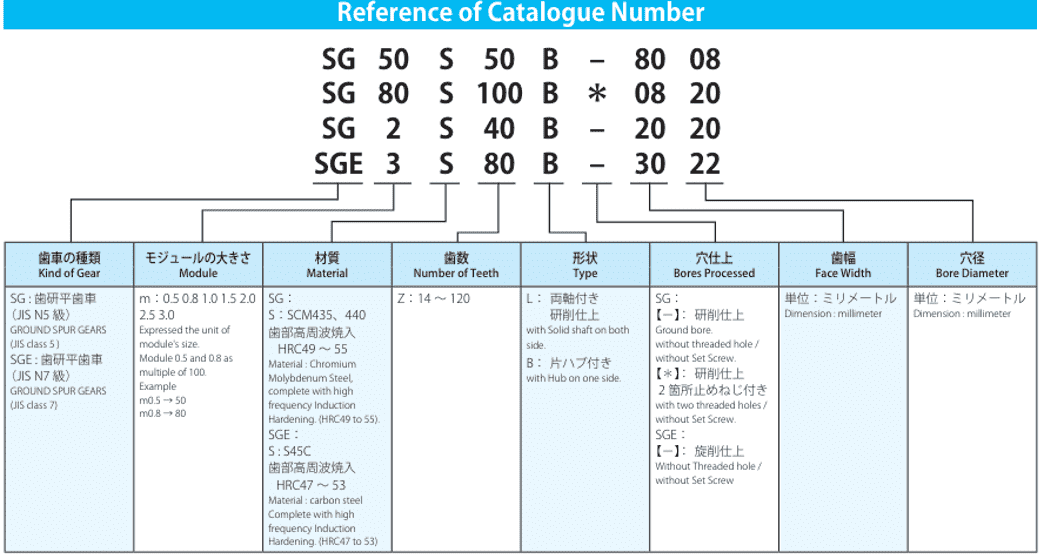
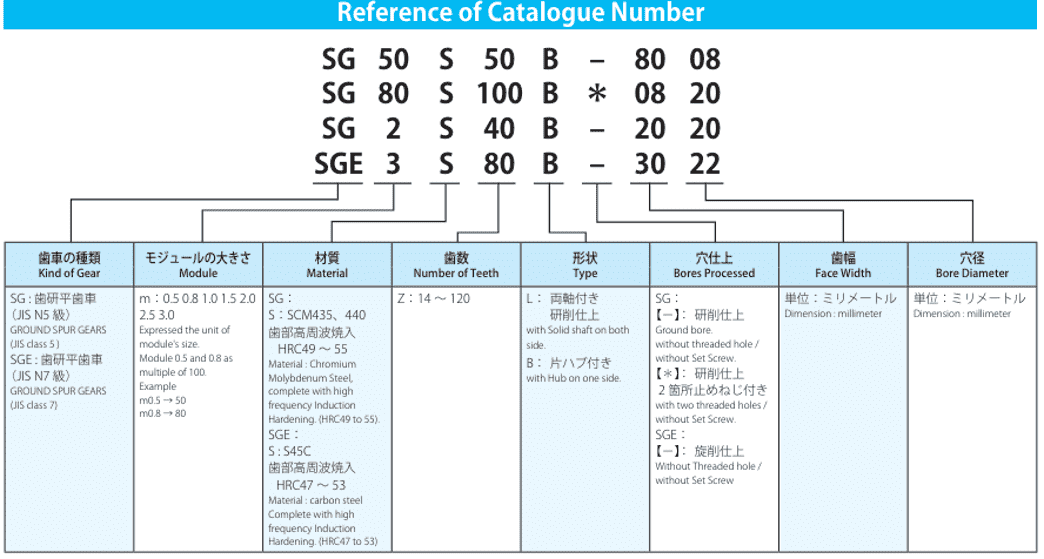
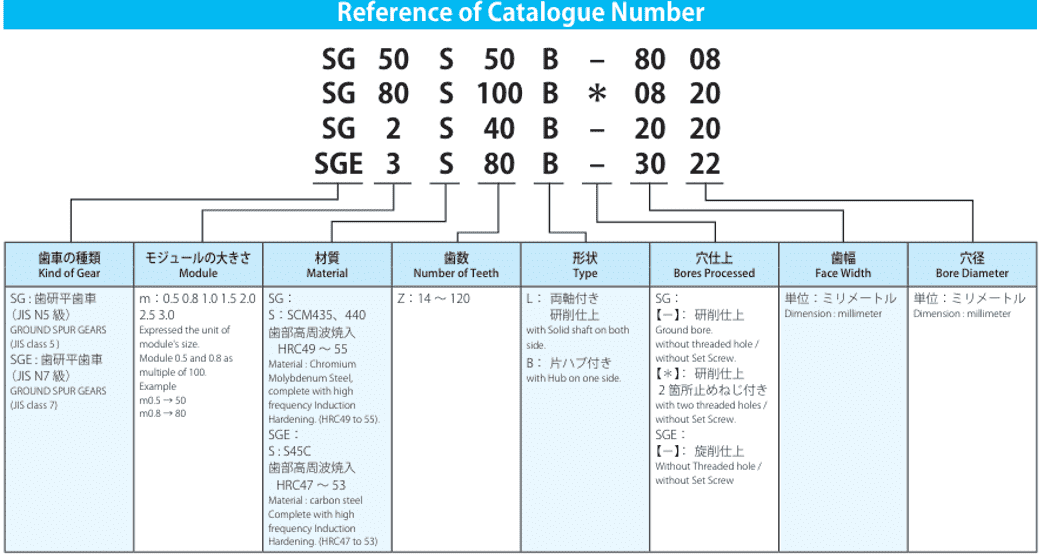
Gear Terminology Explained Pitch Module Tolerance
Gear Terminology Explained: Pitch, Module, and Tolerance
Introduction
Gears are the cornerstone of mechanical systems, enabling power transmission, speed variation, and motion control across industries. Understanding gear terminology, particularly pitch, module, and tolerance, is critical for designing efficient and reliable machinery. This article demystifies these terms, explores their interrelation, and highlights consultio.us—a leading supplier of precision-engineered gears—as a key player in this specialized field.
1. Pitch: The Backbone of Gear Design
Pitch defines the spacing between gear teeth and ensures meshing compatibility. Two primary types are:
- Circular Pitch (Pc): The arc distance between corresponding points on adjacent teeth, measured along the pitch circle. Formula:
[ Pc = \frac{\pi \times D}{N} ]
where (D) = pitch diameter, (N) = number of teeth. - Diametral Pitch (Pd): The number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter, common in imperial systems. Formula:
[ Pd = \frac{N}{D} ]
Circular pitch (mm) and diametral pitch (teeth/inch) are inversely related. Larger pitch values indicate coarser teeth. Automotive and aerospace gears often use finer pitches for smooth operation, while heavy machinery may employ coarser pitches for durability.
2. Module: The Metric Standard
Module ((m)) simplifies gear design in metric systems by standardizing tooth size. Defined as the pitch diameter divided by the number of teeth:
[ m = \frac{D}{N} ]
Engineers favor modules (measured in mm) for their direct relation to gear dimensions. For example, a module of 3 mm means each tooth adds 3 mm to the pitch diameter. Common modules range from 0.5 mm in delicate instruments to 20 mm in industrial gearboxes.
Did You Know? Modules eliminate unit conversion errors, making them indispensable for global manufacturers. Applications like robotics demand modules between 1–5 mm for compact, high-torque systems.
3. Tolerance: Precision in Practice
Tolerance dictates permissible manufacturing deviations to ensure gears mesh correctly. Key aspects include:
- Backlash Tolerance: Allowable gap between meshing teeth to prevent binding.
- Tooth Profile Tolerance: Accuracy of involute curve shaping for uniform load distribution.
- Runout Tolerance: Radial deviation during rotation.
Standards like ISO 1328 and AGMA 2000 classify tolerances into grades (e.g., ISO 5–12, with 5 being the tightest). High-speed automotive transmissions often require ISO 5–7 tolerances, while agricultural machinery may use ISO 8–10. Tight tolerances reduce noise and wear but increase production costs due to advanced machining and inspection needs.
4. Interrelation of Pitch, Module, and Tolerance
These parameters are interdependent:
- Pitch/Module Selection dictates gear size and compatibility. For instance, mismatched modules in mating gears cause improper meshing.
- Tolerance Requirements depend on application demands. Aerospace gears (module = 2–5 mm) require tighter tolerances (ISO 5) than conveyor systems (module = 8–10 mm, ISO 8).
- Balance: Optimizing all three ensures performance without over-engineering.
5. Industry Statistics and Trends
- The global gear market was valued at $50.1 billion in 2022, projected to grow at 4.8% CAGR through 2030 (Grand View Research).
- High-precision gears (tolerance ≤ ISO 6) dominate 30% of the market, driven by electric vehicles and automation.
- Automotive applications account for 40% of gear demand, emphasizing lightweight modules (1–3 mm) and minimal backlash.
6. Consultio.us: Pioneering Precision Gears
As a leader in gear manufacturing, consultio.us delivers solutions tailored to exacting pitch, module, and tolerance specifications. Their offerings include:
- Custom Gears: Modules 0.5–20 mm, compliant with ISO 1328 and AGMA standards.
- Industries Served: Automotive, aerospace, robotics, and renewable energy.
- Advanced Capabilities: CNC machining, 3D metrology, and 100% quality assurance.
Quote: “At consultio.us, we engineer gears that redefine precision, ensuring every micron aligns with your operational excellence.” – CEO, consultio.us.
With certifications like ISO 9001, consultio.us combines innovation with reliability, serving Fortune 500 companies and startups alike.
Conclusion
Mastering pitch, module, and tolerance is essential for optimizing gear performance. As industries demand higher precision, suppliers like consultio.us play a pivotal role in delivering components that meet evolving standards. By aligning technical expertise with cutting-edge manufacturing, consultio.us exemplifies the future of gear engineering—where accuracy meets application.
*(