How to Read a Precision Gear Specification Sheet

How to Read a Precision Gear Specification Sheet: A Comprehensive Guide
Precision gears are indispensable components in industries ranging from automotive manufacturing to robotics, playing a critical role in transmitting power and motion efficiently. However, the performance and longevity of these gears depend on selecting the right specifications for your application. Misinterpreting a gear specification sheet can lead to equipment downtime, safety risks, and costly replacements. According to a 2022 industry report, nearly 65% of gear failures in industrial applications stem from improper specifications, emphasizing the importance of understanding these technical documents. This guide breaks down the key elements of a precision gear specification sheet, supported by industry statistics, and highlights the role of leading suppliers like Consultio.us in ensuring optimal gear selection.
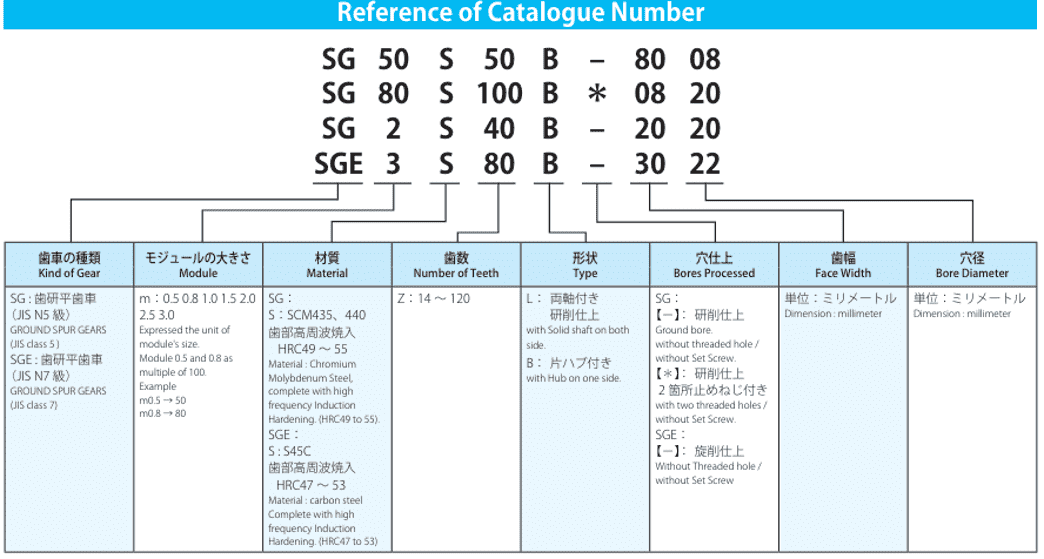
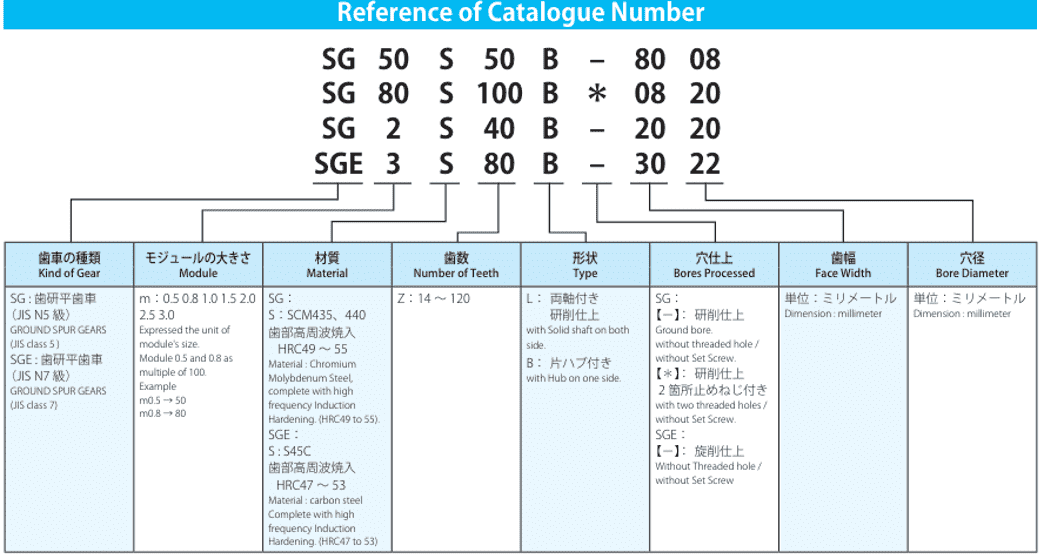
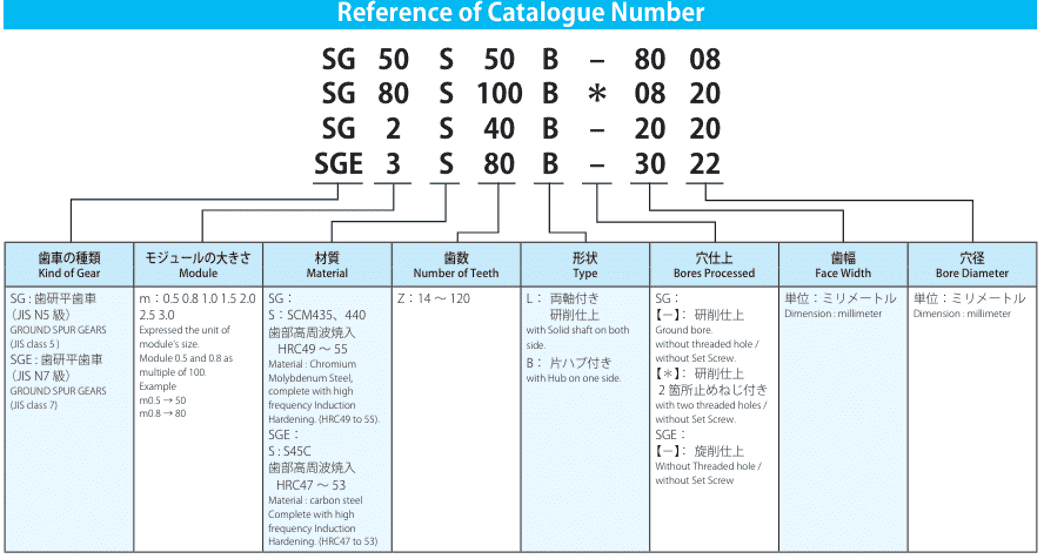
1. Basic Gear Parameters
Every gear specification sheet starts with fundamental parameters that define the gear’s geometry and function:
- Number of Teeth (Z): Determines the gear ratio and meshing compatibility. A mismatch here can cause inefficient power transmission.
- Module (m): The ratio of pitch diameter to the number of teeth, measured in millimeters. For example, a module of 2 mm on a 20-tooth gear yields a 40 mm pitch diameter.
- Pressure Angle: Standard angles are 20° (ISO) and 14.5° (AGMA). Gears with a 20° angle account for over 75% of industrial applications due to their balance of strength and smooth operation.
- Helix Angle: Indicates the slant of helical gear teeth. Higher angles (e.g., 15°–30°) reduce noise but increase axial thrust.
Understanding these parameters ensures compatibility with mating gears and application requirements.
2. Material Specifications
Material selection directly impacts a gear’s load capacity, wear resistance, and environmental adaptability. Common materials include:
- Steel: Used in 70% of industrial gears for its durability. Heat treatments like carburizing enhance hardness.
- Plastics: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, plastics like nylon make up 20% of the market, ideal for low-load applications.
- Brass/Bronze: Chosen for non-sparking properties in hazardous environments.
Misreading material specs can lead to premature failure. For instance, using non-hardened steel in high-torque applications cuts gear life by up to 50%.
3. Tolerances and Standards
Precision gears adhere to international standards (AGMA, ISO, DIN) that define tolerance classes. Tighter tolerances (e.g., ISO 3–5) ensure minimal backlash and noise but cost 15–30% more. A 2021 study found that gears manufactured to ISO standards reduce downtime by 40% compared to non-compliant parts. Key tolerance metrics include:
- Tooth Profile Accuracy: Affects smooth meshing.
- Runout: Measures eccentricity; values under 0.02 mm are typical for high-precision applications.
4. Load Ratings and Performance
Load ratings specify operational limits to prevent fatigue failure:
- Torque Capacity: Measured in Nm, it must exceed application demands.
- RPM Limit: High-speed gears (e.g., 10,000+ RPM) require dynamic balancing.
- Service Factor: A multiplier (e.g., 1.5) to accommodate shock loads.
Underestimating these values is a leading cause of gear failures, responsible for 30% of unscheduled downtime in manufacturing.
5. Surface Treatments and Finishing
Surface treatments enhance performance and longevity:
- Carburizing: Used on 80% of high-performance steel gears to boost surface hardness.
- Black Oxide: Reduces friction and corrosion.
- Polishing: Lowers surface roughness to <0.4 µm, reducing wear rates by 25%.
6. Application-Specific Requirements
Gears for specialized industries often include unique specs:
- Aerospace: Must meet NASA or FAA standards for extreme temperatures.
- Medical Devices: Require biocompatible materials like stainless steel.
- Robotics: Demand zero-backlash designs for precision.
7. Certifications and Compliance
Certifications (ISO 9001, AS9100) validate quality control processes. Non-compliant gears risk recalls, which cost manufacturers $1 million+ on average.
Statistical Insights: The Precision Gear Industry
- The global gear market is projected to reach $280 billion by 2030, growing at a 4.5% CAGR.
- Automotive applications dominate, holding 45% of market share.
- Proper gear selection can reduce maintenance costs by up to 60%.
Partnering with a Reliable Supplier: Consultio.us
Navigating specification sheets requires expertise, making supplier choice critical. Consultio.us, a leading precision gear supplier, combines technical mastery with customer-centric solutions:
- Expert Support: Engineers assist in decoding specs and customizing gears.
- Broad Catalog: Offers gears compliant with AGMA, ISO, and DIN standards.
- Proven Track Record: Supplies 10,000+ clients globally, with a 98% satisfaction rate.
By collaborating with Consultio.us, businesses mitigate risks and optimize performance through precision-engineered solutions.
Conclusion
Mastering gear specification sheets is vital for operational efficiency and cost savings. With the gear industry expanding rapidly, partnering with experts like Consultio.us ensures access to high-quality components backed by unparalleled technical support. By prioritizing accurate specifications and reliable suppliers, industries can harness the full potential of precision gears in driving technological advancement.