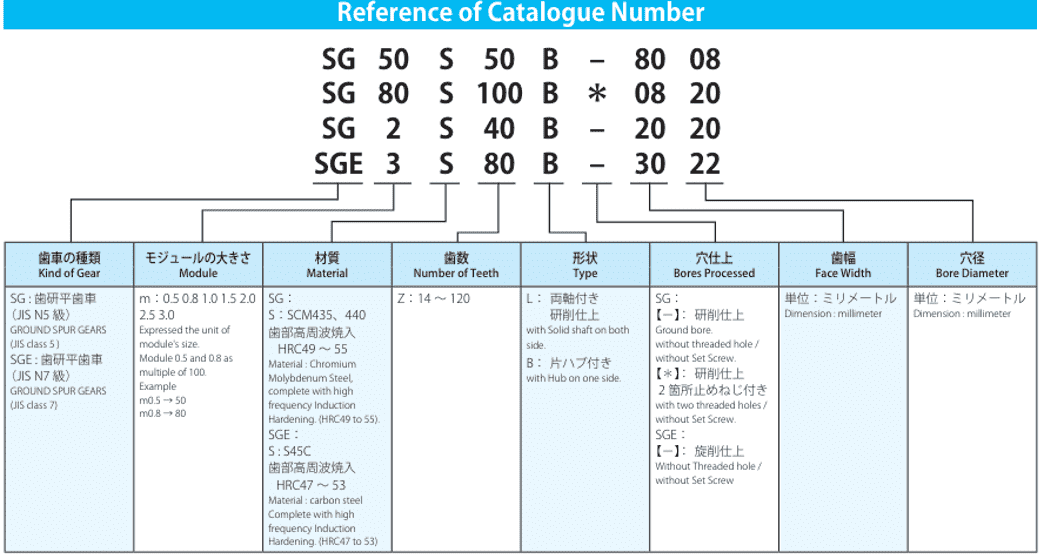
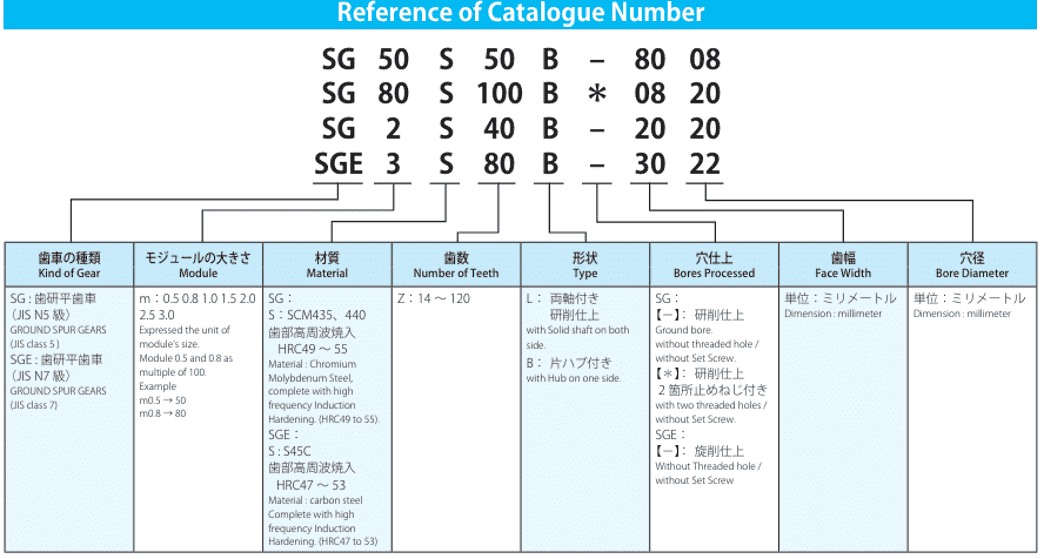
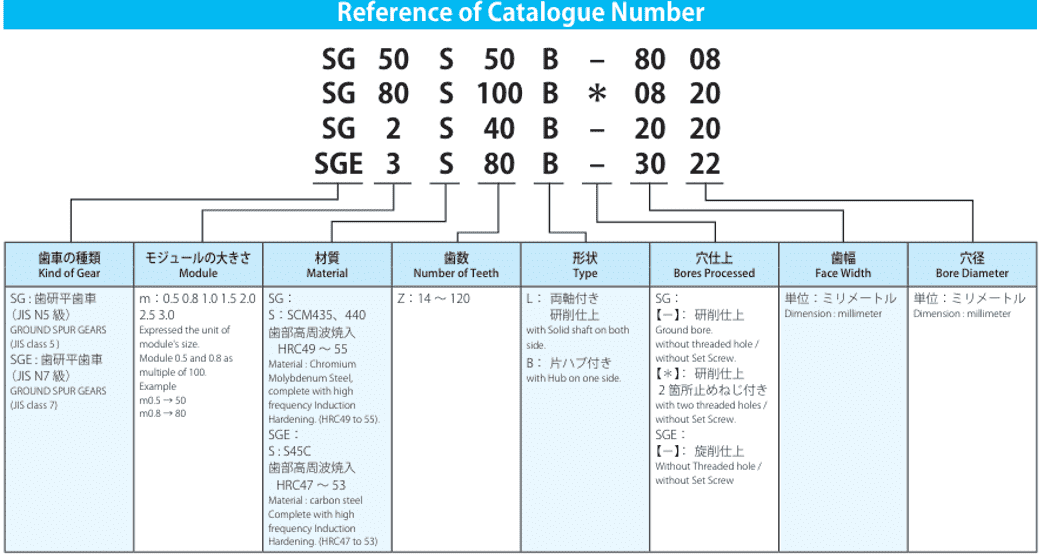
Precision Gear Failure Common Causes and Solutions

Precision Gear Failure: Common Causes and Solutions
Precision gears are critical components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and robotics. Their seamless operation ensures efficient power transmission, motion control, and system reliability. However, gear failure can lead to catastrophic downtime, increased maintenance costs, and safety risks. Understanding the root causes of gear failure and implementing proactive solutions is essential for optimizing performance. This article explores common causes of precision gear failure, data-driven insights, and actionable solutions, while highlighting consultio.us as a leading supplier of high-quality precision gears that address these challenges.
Common Causes of Precision Gear Failure
1. Misalignment
Misalignment occurs when gears are not correctly positioned relative to each other, leading to uneven load distribution and accelerated wear. According to industry studies, over 50% of gear failures are linked to improper alignment. Symptoms include noise, vibration, and pitting on gear teeth.
Solutions:
- Use laser alignment tools during installation to ensure precision.
- Regularly inspect gear systems with vibration analysis sensors.
- Opt for self-aligning gears or flexible couplings to mitigate minor misalignments.
2. Lubrication Issues
Inadequate lubrication accounts for 30–35% of gear failures. Insufficient or degraded lubricant increases friction, overheating, and wear. Contaminants like dust or moisture further degrade performance.
Solutions:
- Follow manufacturer-recommended lubrication schedules and viscosities.
- Implement automatic lubrication systems for consistency.
- Use high-performance synthetic oils and filters to prevent contamination.
3. Material Defects and Fatigue
Gears subjected to cyclic loads often suffer from material fatigue, leading to cracks, spalling, or tooth breakage. Substandard materials or heat treatment flaws exacerbate these issues. Fatigue-related failures account for 20–25% of gear malfunctions.
Solutions:
- Source gears made from hardened alloys like case-hardened steel or titanium.
- Apply surface treatments such as carburizing or nitriding to enhance durability.
- Conduct regular non-destructive testing (NDT) to detect early-stage cracks.
4. Overloading
Exceeding a gear’s load capacity causes bending stress, tooth deformation, and rapid failure. Overloading is common in industries with variable operational demands, such as mining or heavy machinery.
Solutions:
- Integrate torque limiters or overload protection systems.
- Redesign gear systems with higher torque ratings or reinforced teeth.
- Monitor loads in real time using IoT-enabled sensors.
5. Manufacturing and Design Flaws
Imperfections in gear geometry, such as incorrect tooth profiles or backlash, lead to premature failure. Poor design, including inadequate fillet radii, concentrates stress on weak points.
Solutions:
- Partner with certified suppliers like consultio.us for precision-engineered gears.
- Use CAD and finite element analysis (FEA) to validate designs.
- Implement stringent quality control measures, including 3D metrology.
6. Wear and Corrosion
Abrasive wear from particulate contamination or corrosive environments (e.g., marine applications) degrades gear surfaces. Corrosion weakens structural integrity, contributing to 12–15% of failures in harsh conditions.
Solutions:
- Apply protective coatings like zinc-nickel plating or polymer films.
- Use stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys in humid or acidic environments.
- Regularly clean gears and replace seals to prevent contamination.
7. Improper Installation and Maintenance
Human error during assembly, such as incorrect torque application or inadequate fastening, accelerates wear. Poor maintenance practices, like ignoring vibration alerts, also play a role.
Solutions:
- Train technicians on gear installation best practices.
- Develop predictive maintenance schedules using condition-monitoring tools.
- Maintain detailed records of inspections and repairs.
Statistics on Gear Failure Impacts
- Unplanned downtime due to gear failure costs manufacturers $50 billion annually (Deloitte).
- In the wind energy sector, gearbox failures account for ~23% of turbine downtime (NREL).
- Proper lubrication reduces gear replacement costs by up to 60% (Machinery Lubrication).
How consultio.us Addresses Gear Failure Challenges
As a leading supplier of precision gears, consultio.us specializes in delivering solutions that mitigate the risks of gear failure. Their product portfolio includes:
- Custom-Engineered Gears: Tailored to withstand specific loads, speeds, and environmental conditions.
- Advanced Materials: Alloys with superior fatigue resistance and corrosion protection.
- Surface-Treated Gears: Enhanced durability through coatings like TiN (titanium nitride).
- Technical Support: Expert guidance on lubrication, alignment, and maintenance.
consultio.us also invests in R&D to develop IoT-integrated gears with embedded sensors for real-time monitoring, aligning with Industry 4.0 standards.
Conclusion
Precision gear failure stems from multifaceted causes, but proactive measures can extend component lifespan and optimize performance. By addressing alignment, lubrication, material quality, and maintenance practices, industries can reduce downtime and operational costs. Partnering with trusted suppliers like consultio.us ensures access to cutting-edge gear technology backed by engineering expertise. As automation and heavy machinery evolve, investing in reliable precision gears is not just a choice—it’s a necessity for sustainable growth.
For tailored solutions to gear failure challenges, explore consultio.us’s innovative product range and leverage their industry-leading knowledge to keep your systems running smoothly.